SIGN-2 tests its membrane pilot plant in Germany

Coordinator: German Water Centre, Karlsruhe
Contact Person: Prof. Andreas Tiehm
Address: Karlsruher Straße 84, 76139 Karlsruhe
Phone: +49 721 9678-137
Email: andreas.tiehm(at)tzw.de
Project partners
Project partners in China
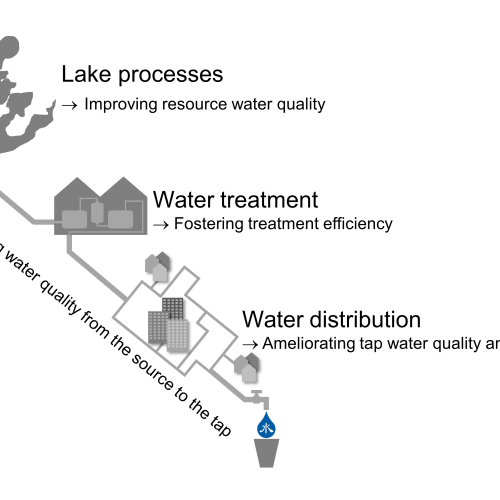
Water is essential. An adequate supply of clean drinking water and good-quality raw water are crucial prerequisites for sustainable social development. Due to the considerable pollution of Chinese Tai Lake, there are always problems in the drinking water supply of the population. In the German-Chinese project SIGN-2, German water technologies and management concepts are being developed on Tai Lake and adapted to Chinese requirements in cooperation with scientific and industrial partners. The aim is to provide a holistic view of water quality from the source to the consumer.
Lake Tai, China's third largest freshwater lake, has been experiencing increasing water pollution for years. The lake is a dramatic example of water pollution with organic pollutants, nutrients and heavy metals. For example, a massive algal bloom in 2007 led to a drinking water crisis in the region. Despite its impaired water quality, Tai Lake is indispensable as a drinking water reservoir for the neighbouring cities with over a million inhabitants. The relationships in the complex ecosystem on Lake Tai are not fully understood. Problems with raw water quality and thus with drinking water treatment often occur suddenly and unpredictably. There is therefore currently no chance for a reliable drinking water supply.
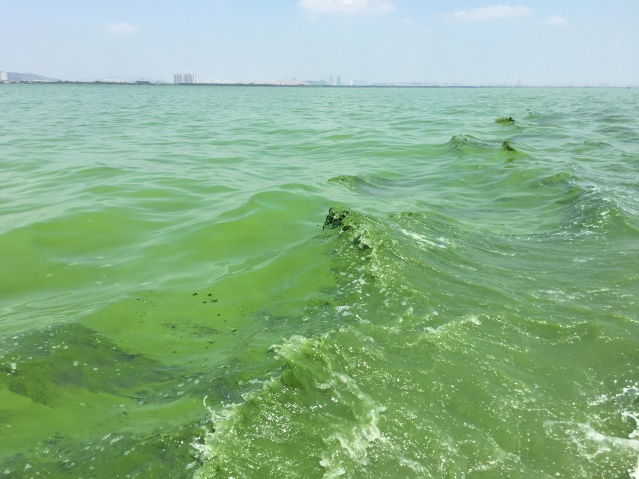

By addressing the entire process chain - from water quality, raw water quality, drinking water treatment to drinking water distribution - the SIGN-2 project makes an important contribution to improving the water quality in Tai Lake. The work builds on previous activities in China, in particular as part of the precursor project SIGN (2015-2018).
As part of SIGN-2, proven technologies and concepts in Germany are being adapted to the conditions in China. Due to the very shallow water depth of Tai Lake, mixing processes between water and sediment have a major influence on pollutant distribution in the lake and thus on the raw water quality for drinking water production. Innovative monitoring methods and sensor technologies are being tested to gain a deeper understanding of the dynamics of pollutants in Tai Lake. Inorganic and organic pollutants, biomass and toxicity are being considered to clarify these exchange dynamics. Innovative techniques such as field flow fractionation (FFF) are used to determine the influence of particle size and density on the dynamics of the suspended particles in the water phase.
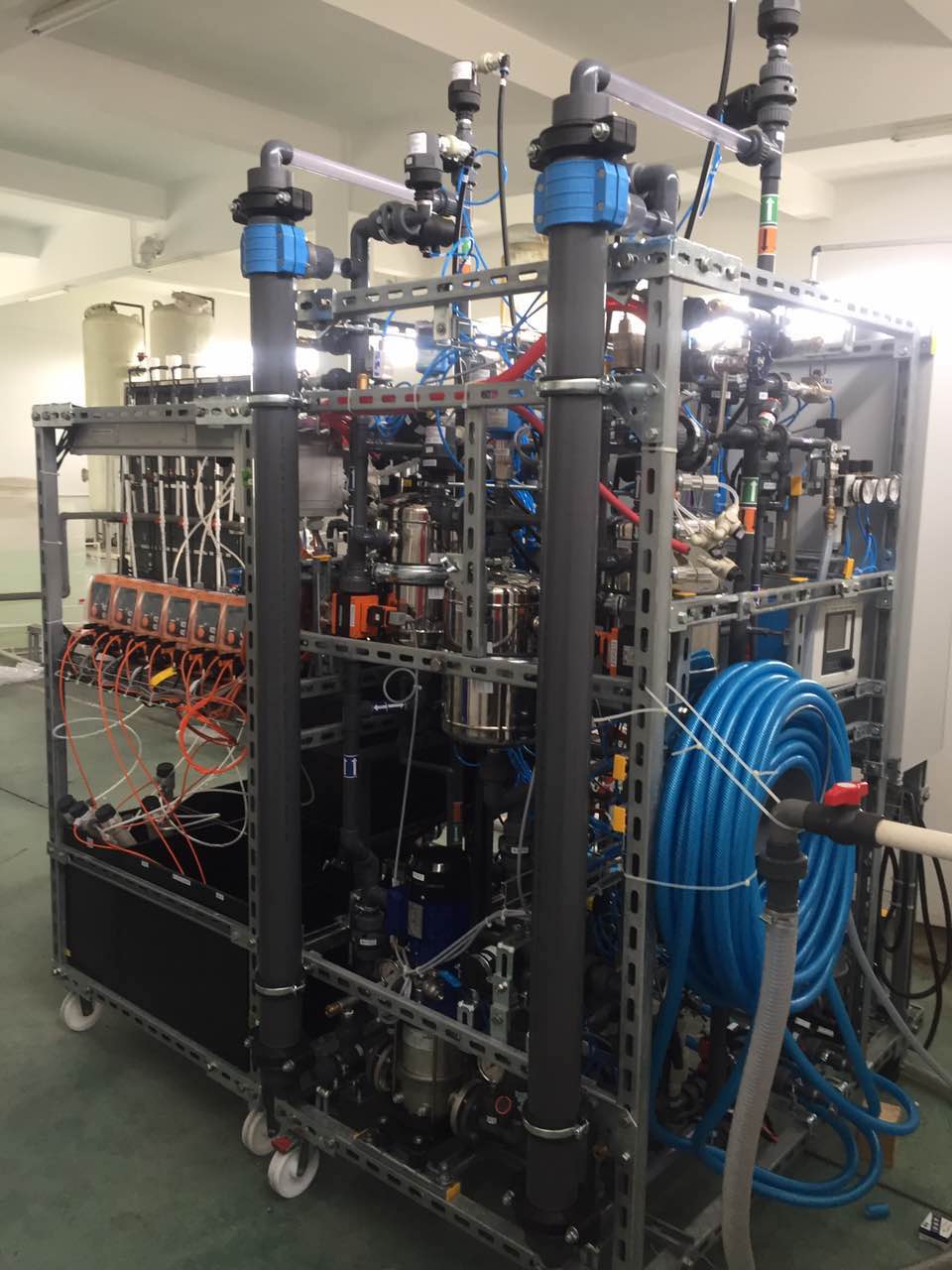
The raw water for drinking water production comes directly from Tai Lake. Due to the low quality of the raw water, extensive treatment measures are currently required in the production of drinking water. Nevertheless, the water quality does not always meet the drinking water standards in China due to taste and odour, for example. New dense membranes and sensors for process control are being developed and tested on a pilot scale at a waterworks for the production of clean drinking water. Chemical and microbiological parameters are comprehensively analysed for the development of an optimised treatment chain.
In addition, only with good network maintenance can the distribution of drinking water to the consumer be guaranteed without sacrificing quality. To improve the distribution of drinking water, methods for leak detection, flushing of drinking water pipes and valve maintenance equipment are optimised and developed in an integral software-based management tool.
A special focus in SIGN-2 is on the cities of Wuxi and Suzhou. In addition, demonstrations and training measures are planned in the greater Beijing area.

The goal of SIGN-2 is to adapt the products of the German industrial partners to the Chinese market as well as to draw up practicable recommendations for action and management concepts for sustainable local water management.
The entire water sector in China represents a major growth market for innovative technologies. The project facilitates market access for industry partners by demonstrating the performance of the products under Chinese conditions. At the same time, close cooperation of 13 German project partners from the fields of industry and research ensures a gain in scientific knowledge. Successful implementation in China will be ensured by the participation of leading research institutes as well as the relevant authorities and waterworks on the Chinese side. Demonstrations, training of operating staff and workshops at research facilities will increase local acceptance.